
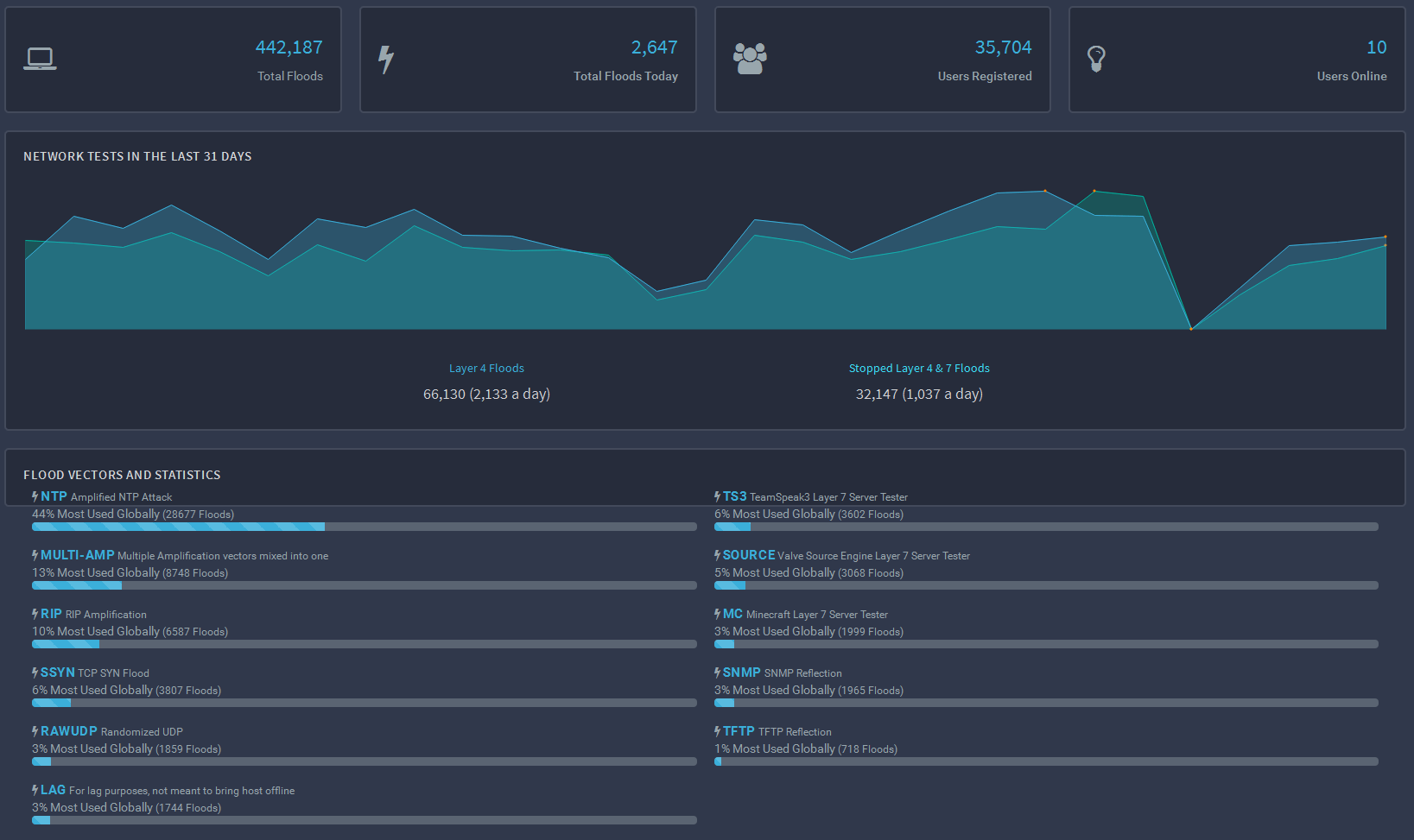
Widespread flooding attacks include buffer overflow attacks, ICMP floods, and SYN floods.Ĭrashing exploits flaws in the target system or service, causing the target to crash. Flooding occurs when the system receives excessive traffic that the server cannot buffer, leading the system to slow down and eventually cease operations altogether. This article explains these differences, as well as how users can prevent DoS and DDoS attacks.ĭoS attacks can be classified into two broad categories: flooding services and crashing services.

In either attack, the goal is to blend in as much as possible, making mitigation efforts as inefficient as possible.īeing familiar with the different types of DoS and DDoS attacks that may occur is an essential component of internet security. A DDoS attack is launched utilizing thousands, even hundreds of thousands, of unwitting zombie PCs. A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, on the other hand, is a DoS attack that originates from multiple sources simultaneously. During the attack, regular website traffic will be interrupted – either slowed down or altogether halted. A DoS attack aims to render a website unavailable to users by flooding the target URL with more requests than the server can handle. The simplicity and efficiency with which a DoS attack may be orchestrated make denial of service an attractive method for cybercriminals or hacktivists. Denial of service (DoS) attacks have become one of the most widespread cybersecurity dangers confronting modern businesses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
